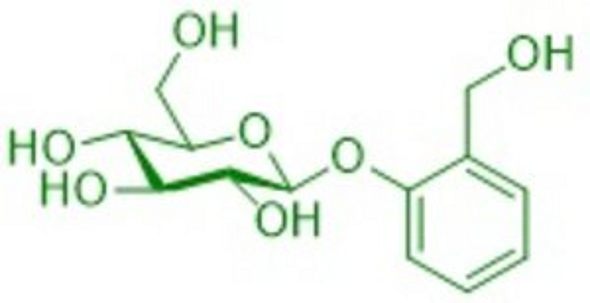
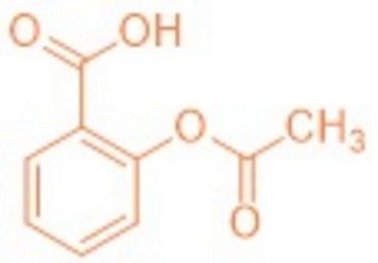
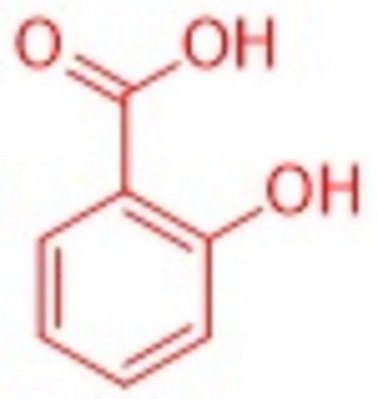
How is a drug developed? Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) certainly reflects the progress made in active ingredient research like no other drug. Willow bark extracts were already being used in ancient times to treat inflammation. Salicin is responsible for the effect, from which the actual active ingredient, salicylic acid, is formed through decomposition and oxidation. A Nobel Prize was awarded in 1982 for the partial elucidation of the astonishing mechanism of action of aspirin (Vane, England).
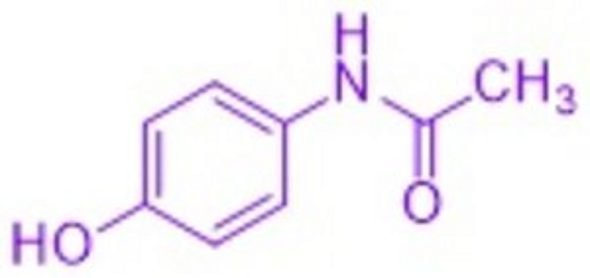
The development of p-hydroxyacetanilide(paracetamol) actually goes back to a waste product from the paint industry. Annual sales of this antipyretic drug in the USA today amount to USD 13 million and are therefore even higher than those of aspirin.